In the world of SEO, we often get so wrapped up in the quest for keywords, backlinks, and high-quality content that we overlook a critical component: technical SEO. Technical SEO refers to the nuts and bolts of your website—its structure, security, speed, and more. It’s the foundation on which all your other SEO efforts are built. And yet, it’s all too often neglected, which can result in a website that’s trying to climb the search engine rankings with one hand tied behind its back.
This ultimate technical SEO checklist for 2023 is here to help you change that. It’s time to give your website the technical tune-up it needs to really shine in search engine results.
1. Identify Crawl Errors
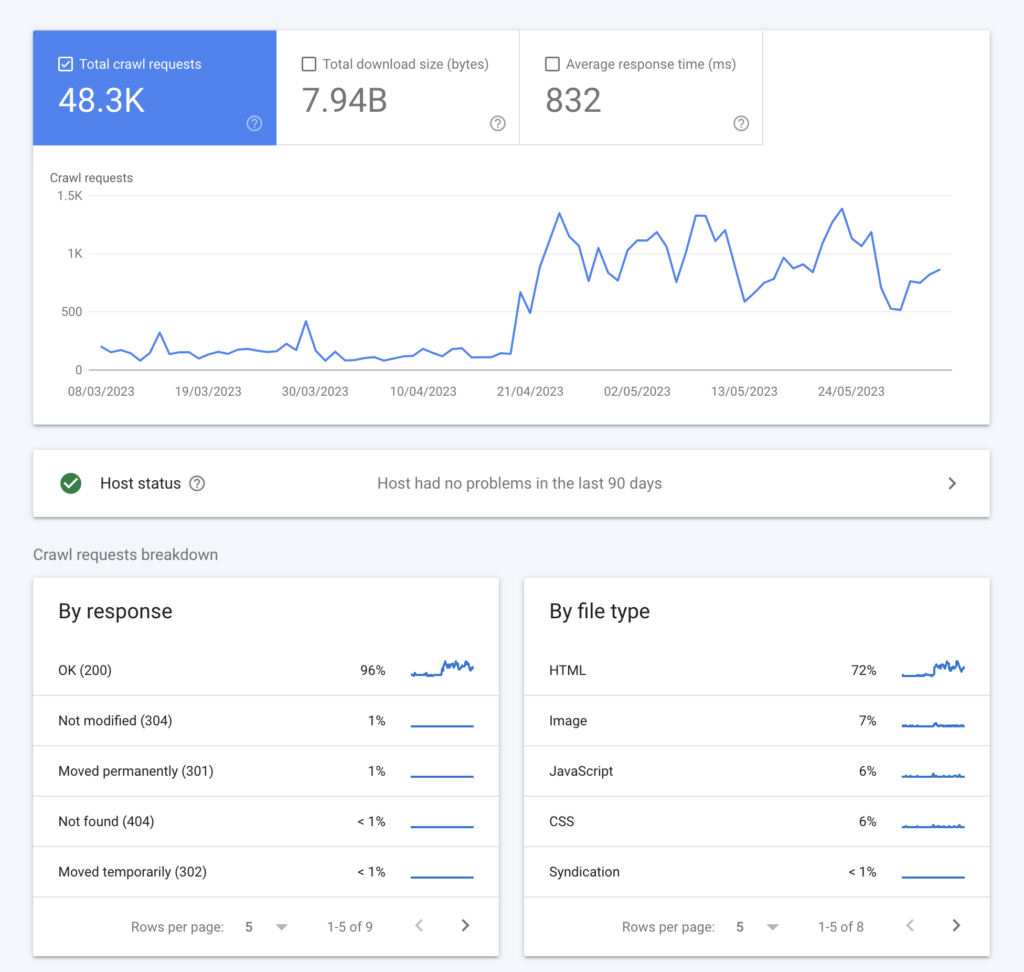
Crawl errors occur when Google has trouble viewing a page on your site. If Google can’t view your page, it won’t rank. You can easily find crawl errors in the Google Search Console’s “Coverage” report. If you notice Google is having trouble accessing one of your important web pages (for example, robots.txt is blocking search engine spiders), you’ll want to get that fixed ASAP.
Common crawl errors include:
- 404 Not Found: This error occurs when the page that Google is trying to access doesn’t exist. This might be because the page has been deleted, or the URL has been changed without a redirect being set up.
- Access Denied: These errors occur when Googlebot doesn’t have permission to access a page on your site. This might be because the page is blocked by your robots.txt file, or because it requires a password to access.
- Server Error: These errors occur when there’s a problem with your server. This could be because your site is down, or because there’s a problem with your server’s configuration.
To fix these errors, you should:
- Fix Broken or Outdated Links: If a page on your site doesn’t exist anymore, make sure there are no links pointing to it. If the content has been moved to a new URL, set up a 301 redirect to guide Google (and your users) to the new location.
- Update Your Robots.txt File: If you’re blocking Google from accessing certain pages, make sure it’s intentional. If not, update your robots.txt file to allow Google to access these pages.
- Ensure Your Server is Running Smoothly: Regularly check your server’s health and address any issues that might be causing downtime or slow response times.
It’s completely understandable that you don’t have the technical knowledge to fix these crawling errors. Try contacting a developer to help you out, as these issues are important!
2. Find Out How Google Views Your Page
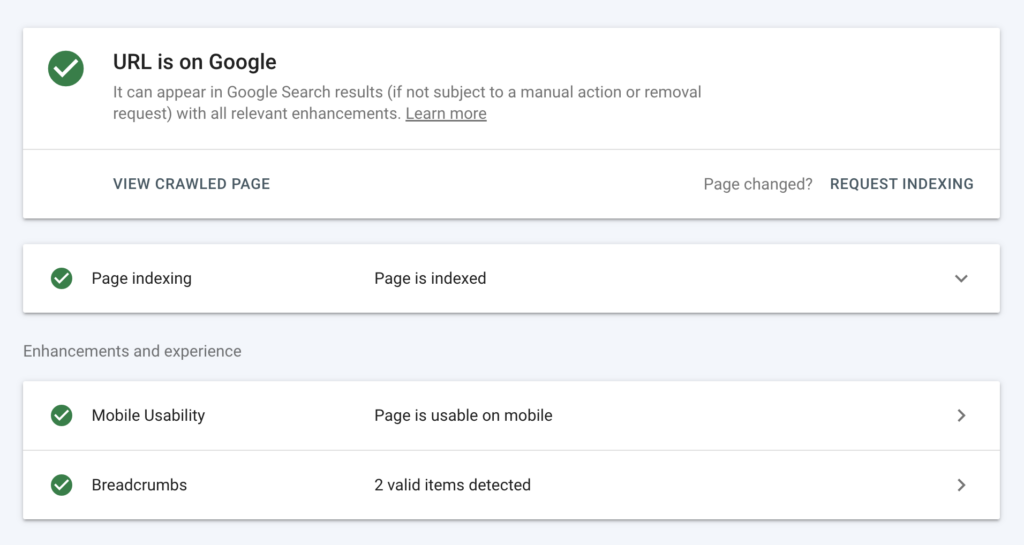
Sometimes users can see everything on your page, but Google can’t. If Google can’t fully access your page, it won’t rank. That’s why it’s recommended to use the Google Search Console’s “Inspect URL” feature. Enter a page from your site at the top of the GSC. When you do, you’ll see your page from Google’s point of view. This tool is very helpful for understanding how your page appears to search engines.
3. Make Sure Your Site is Mobile-Friendly
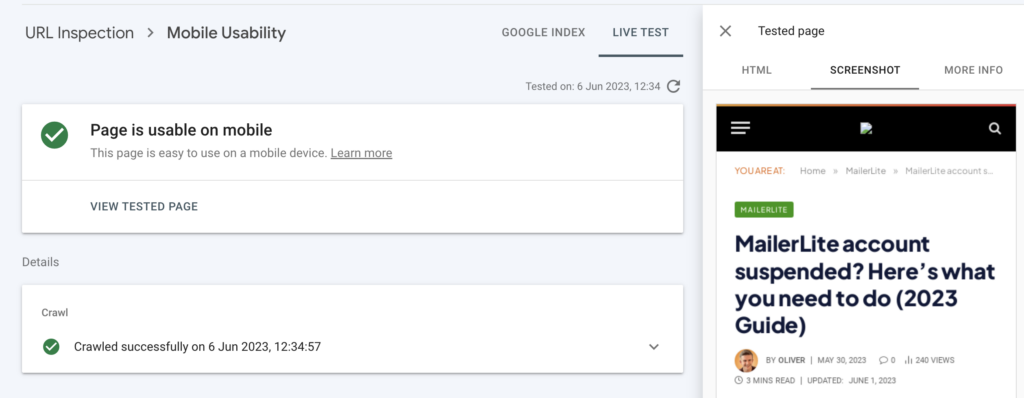
With Google’s recent launch of the “Mobile-First Index,” if your site isn’t mobile-optimized, it won’t rank very well. Fortunately, you can easily check your site’s mobile friendliness with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test. Just pop in a page from your site and get a clear “yes or no” answer.
4. Fix Broken Links
Broken links can be a real thorn in the side of your SEO efforts. These are links on your site that point to non-existent resources. They can be either internal (i.e., to other pages on your domain) or external (i.e., to pages on other domains). Broken links can end up on your website in two ways: either the linked-to site deletes or removes the page you are linking to, or you inadvertently link to the wrong URL. Broken links can waste “link juice” and hinder your website’s crawlability, both of which are detrimental to your SEO. Plus, they lead to a poor user experience, which can hurt your site’s reputation with users and search engines alike.
How do you go about fixing broken links? Here are the steps:
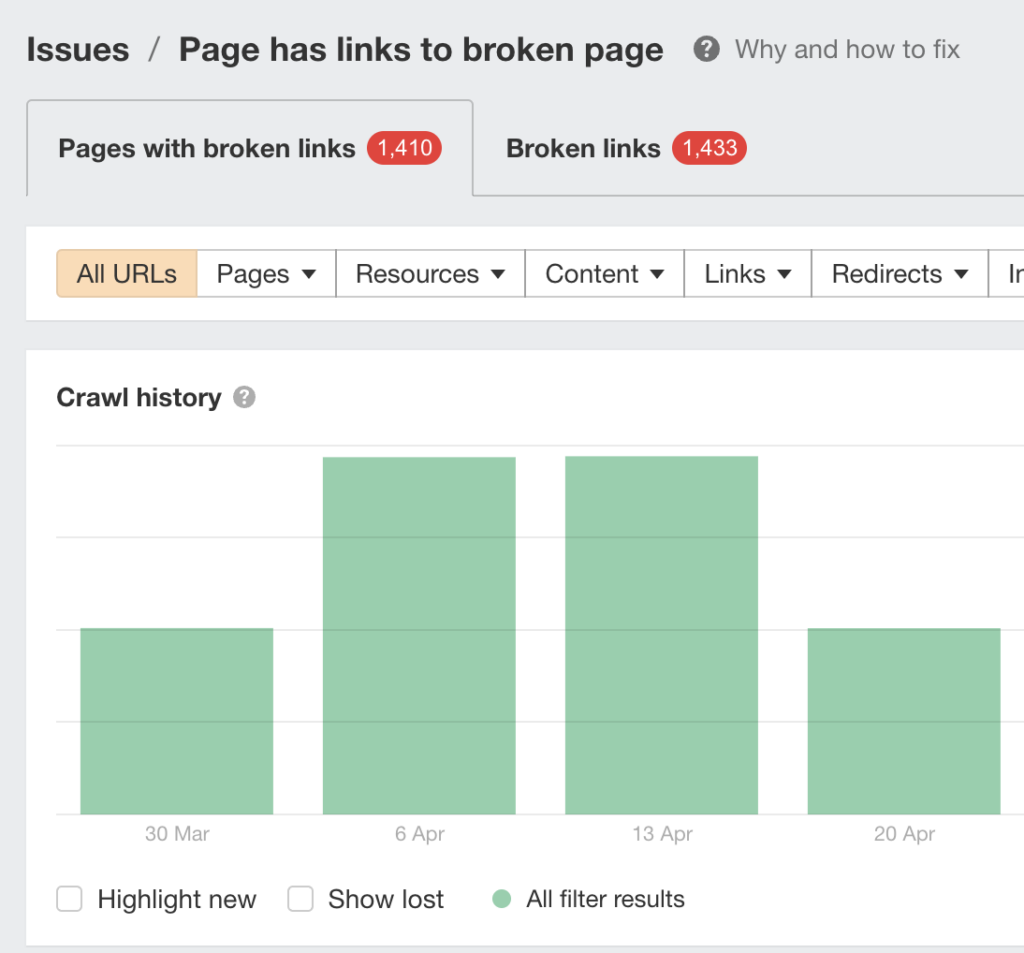
Step #1: Finding ALL Broken Links on Your Site
For smaller websites, you can use tools like Ahrefs’ Site Explorer to find all broken external links. But for larger websites, it’s better to use a tool like Ahrefs’ Site Audit or Google’s Search Console, which will perform a live crawl of your website and ensure that you don’t miss any broken links. These tools can show you both broken external links and broken internal links.
Step #2: Fixing ALL Broken Links on Your Site
Once you’ve identified your broken links, it’s time to fix them. This process can be time-consuming, but it’s relatively straightforward. There are two main ways to fix broken links:
- Replace the Broken Links with Live Links: Find a replacement for the broken link, then replace it on your site. If you’re not sure what the link used to point to, try using the Wayback Machine to see an archived version of the page.
- Remove the Links: If there’s no suitable replacement for a broken link, or if the link isn’t necessary, you can simply remove it from your site.
Remember, fixing broken links is an essential part of maintaining your site’s technical SEO and ensuring a positive user experience. It may be a somewhat tedious task, but it’s well worth the effort in terms of the benefits it can bring to your site’s performance in search engine rankings.
5. Secure Your Site With HTTPS
HTTPS is a confirmed Google ranking signal. So if you haven’t already, it’s time to move your site to HTTPS. If you’ve just launched a new site, set it up with HTTPS from day one. Securing your site with HTTPS is critical for user trust, site security, and improved rankings. There are many guides available to help you migrate your site to HTTPS without hurting your SEO.

6. Check Your Site’s Loading Speed
If your site doesn’t load quickly, it won’t rank as well. Site speed is a critical ranking factor, and slow-loading pages can lead to high bounce rates. PageSpeed Insights is a free tool that lets you know how quickly your site loads for desktop and mobile users. The tool also provides suggestions on what you can do to speed things up. Regularly checking your site’s loading speed and implementing the recommended optimizations can significantly improve user experience and boost your site’s visibility in search engine results.
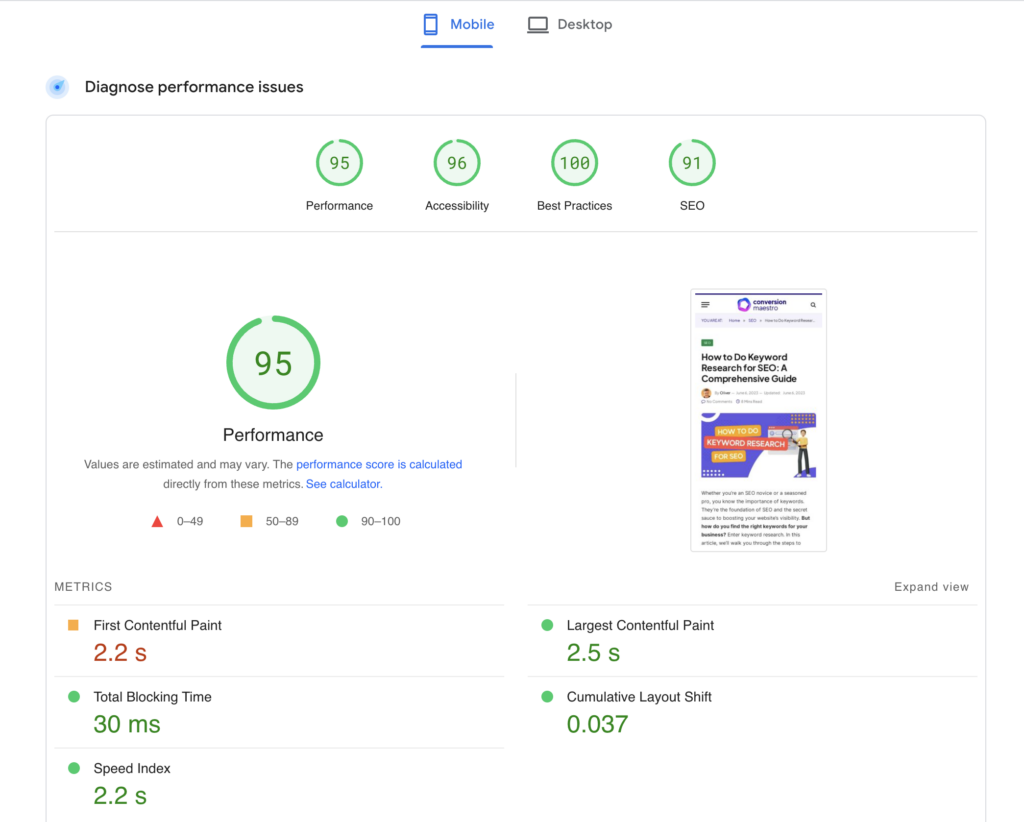
Here are a few quick fixes to speed up your site:
- Compress Images: Large, high-resolution images can slow down your site. Use an image compression tool to reduce the file size of your images without sacrificing quality.
- Enable Browser Caching: When you enable browser caching, return visitors to your site won’t have to reload the entire page—only the new or changed content. This can significantly improve your site’s speed.
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML: “Minifying” these elements removes unnecessary characters (like spaces and commas) from your site’s code, which can help it run faster.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN can distribute your content across multiple servers around the world, which can help it load faster for users no matter where they are.
By focusing on these areas, you can make a significant improvement in your site’s loading speed, which can lead to better user experience, lower bounce rates, and improved search engine rankings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, technical SEO is an essential part of your overall SEO strategy. By following this checklist, you can identify and fix technical issues that might be hampering your site’s performance in search engine rankings. So start implementing these practices and see your website climb the SERPs in 2023.

